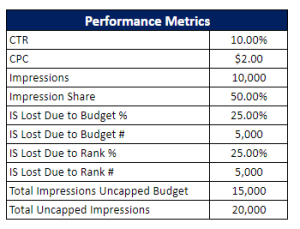
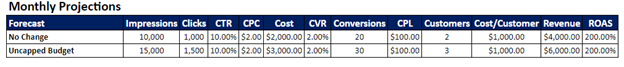
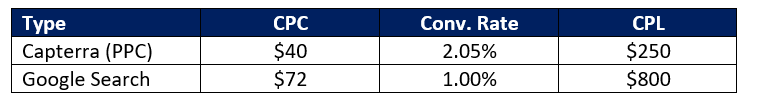
No matter where you stand on AI, it’s no longer something we can ignore. In 2022 alone, AI companies received $1.37 billion in venture capital — which is more than in the previous five years combined. And businesses are taking note. According to a recent survey from IBM, 77 percent of businesses used or explored AI solutions in 2022. Around half of these organizations were already seeing the benefits of AI-powered tools to automate business processes, increase efficiencies, and provide better experiences for their customers, across a variety of industries.
In sales and marketing specifically, 30 percent of adopters reported up to a 10 percent increase in revenue after implementing AI technology.
As technology advances, so too must our digital marketing strategies. Because let’s face it: AI has transformed the search experience. Google uses AI in its algorithms. AI bots like ChatGPT are putting quick answers—and research—right at our fingertips. And AI-powered writing assistants are becoming increasingly popular to create web-based content and improve efficiencies across marketing teams.
Synapse SEM has investigated, trialed, and tested several popular AI tools on the market, to understand their value and potential application in the search engine optimization (SEO) space. We’ve also explored Google’s perspective on AI in relation to content creation for SEO, and compiled recommendations for how to use AI effectively in your SEO strategy. Let’s dive in.
5 Ways Businesses Can Use AI to Enhance Their SEO Strategy
Before delving into the possible AI tools that marketing professionals can use, let’s first cover what they can be used for. Here are some of the many use cases we’ve identified for AI-powered platforms in the world of search engine optimization.
- Early Keyword Research
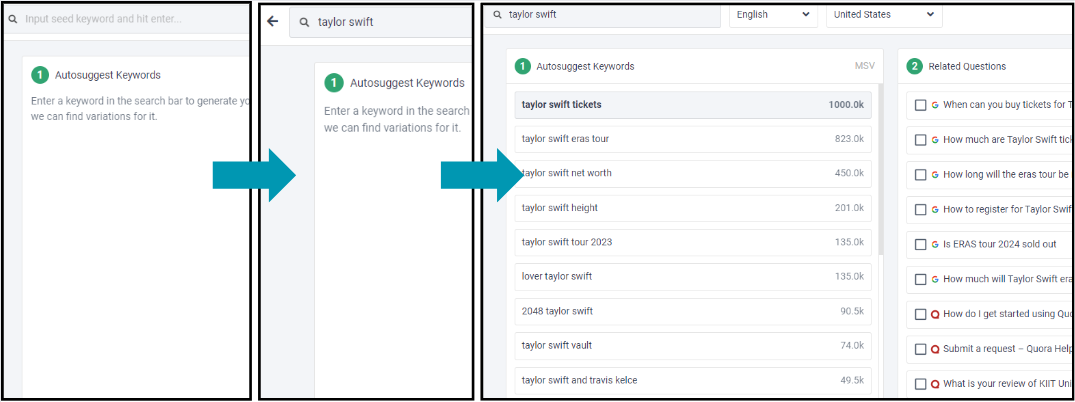
AI SEO tools can be used to curate lists of popular keywords related to a given topic. Depending on the platform being used, there may be a dedicated feature for keyword research. Or, if you are using an AI chatbot like ChatGPT, you can simply ask it to generate a list of keywords related to your query. However, there are limitations to this, which is why we suggested “early” keyword research. These tools can provide a jumping point for keyword ideas but should be supplemented with KPIs like search volume, historical conversions, and difficulty.
- Topic Generation and Outlines
Similarly, AI tools can assist in developing blog topic ideas, as well as outlines to support them. For example, you can command an AI bot to craft a catchy headline for a blog post. An AI tool can also generate an outline for you, providing key bullet points to hit on in your article, and suggesting various subheadings to use throughout. However, it’s important to remember that these tools do not provide data-driven recommendations. They do not always know the full competitive landscape around a topic, or the search volume behind semantic keyword phrases. Therefore, use these tools for inspiration—but consider some outside research, too.
- Content Generation
There are a variety of AI content generators out there now, that can literally write content for you. From Jasper.ai to Frase.io, these tools have the power to write long-form content with a little guidance from the user. You can say, “Write a blog post about the impact of AI on SEO” or, “Write a paragraph about popular AI writing tools.” An AI bot will quickly gather and process content from all corners of the web, to put together a one-of-a-kind piece that you can use for marketing purposes. However, be aware: These tools are borrowing information from other web pages. While they will not copy content word-for-word, they will create summaries of what others are saying. They may not provide the real value you are looking for (or the real value that you need to rank highly in Google today). Further, it is not possible to know whether the information they provide is accurate. AI writers have the potential to fill your content with inaccurate, unreliable, or simply uncited research – therefore requiring a human-grade QA.
- Meta Tags and Website Coding
Several SEO-focused AI tools are familiar with the basic best practices of meta tag generation. For example, Frase and Jasper both have tools that can craft meta descriptions for your page, with just a little direction provided. They will provide a handful of options, within the recommended character count, for your selection, using the same logic as their writing assistants. Other AI tools, ChatGPT being one example, can help you with the development of code to use on the back-end of a website. For example, I asked ChatGPT to provide me with the HTML code for a meta description. It said:
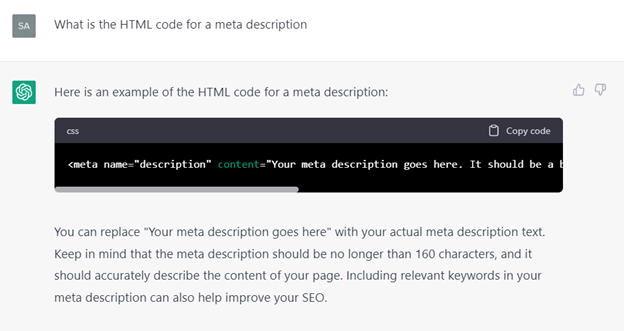
However, a meta description is just one example of the many codes ChatGPT can provide. You can also ask this AI chatbot about Schema Markup, noindex and nofollow tags, Robots.txt coding, and more. Always be sure to QA what the AI tool provides you, though, as ChatGPT bases its recommendations only on learnings from other web results (and they may not be accurate).
- Content Syndication and Link Building
Just as AI-assisting writing tools can build content for your website, they can also build content for your social media posts. How does this impact SEO, you might ask? Sharing your content on social media is an important part of increasing your brand’s visibility, and has the potential to attract backlinks to your site. You can use AI to help craft engaging social media posts that feature your content. Jasper.ai and Frase.io both have tools to aid in Instagram captions, for example.
Social syndication isn’t the only means of building links, either. Email outreach is another way to get your content in front of a larger audience, and build links back to your brand. You can use an AI-powered platform to develop professional email outreach templates to promote your content, request backlinks, or ask about guest blogging opportunities.
5 Examples of AI SEO Tools that Marketers Love
There are an extensive number of AI-powered tools available to businesses and agencies today. ChatGPT is perhaps one of the latest to hit this list, but the general concepts behind these technologies are similar. For marketing professionals, AI tools are being used to increase efficiencies in content development, ad generation, and website optimization purposes. Here are some examples of the most popular AI tools we came across for SEO purposes:
1. ChatGPT:
ChatGPT is an AI-powered chatbot that was designed to simulate online customer care. However, even that definition is an understatement. Launched in November 2022 by OpenAI, this chatbot has already taken the world by storm. In fact, this AI tool set the record for the fastest-growing platform within just two months of being launched, and recently became one of the 50 most visited websites in the world.
ChatGPT has the power to answer complex questions quickly and perform in-depth tasks, such as generating website code, drafting outreach emails, and—yes—writing content.
The tool is rooted in GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) architecture. This means it has been trained on a large dataset of text and statistics from the internet, and further programmed to accurately craft sentences, generate answers, write articles, as well as learn from its users. It is designed to mirror human-like dialogue.
Of course, I put ChatGPT to the test. When asked how ChatGPT can be leveraged for SEO, it replied:
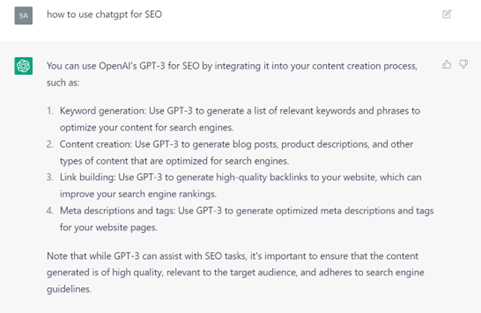
Thanks, ChatGPT! Overall, I found that the tool – when it was accessible (it’s frequently at capacity) – was a great way to get quick answers and topic ideas. For content creators, ChatGPT could be an excellent resource for overcoming writer’s block, generating catchy headlines for blogs, or even developing an outline or bullet points for a forthcoming blog article. However, I would not recommend relying on it for content writing or optimization. This is for two main reasons:
- ChatGPT essentially summarizes what else is on the web. It does not provide uniquely valuable content and may not provide the most helpful content for your readers. Similarly, it may not provide the most accurate information or research, because it’s borrowing from other corners of the web.
- It does not apply competitor insights or best practices to the content it creates. It does not assess the top-ranking websites, understand which headlines would be most effective, or utilize semantic keywords to help your content rank.
With that, I would recommend utilizing ChatGPT as a guiding point for SEO tasks like:
- Blog ideas. ChatGPT can generate outlines, headlines, bullet points, and even statistics to help guide your blog content.
- Code generation. ChatGPT has a good grasp on things like noindex tags, structured data, and meta descriptions. Just remember to QA what ChatGPT recommends—it’s not always accurate.
- Short content inspiration. We don’t want to ignore its content development features, but take them with a grain of salt. Try using ChatGPT to create short snippets, such as for a new Facebook post, product description, or quick blurb to try and get that Featured Snippet.
- Email generation. The content produced by ChatGPT doesn’t need to be applied to websites, but could also be used to craft emails quickly—especially ones being sent in bulk.
2. Jasper AI:
Jasper is an impressive AI platform that generates content about 10 times faster than a human writer. Its primary purpose is for copywriting, but that can be applied to various functions: generating product descriptions, creating listicles for articles, writing introductions and conclusions, developing YouTube topic ideas, creating captions for Instagram, and coming up with compelling headlines for your blog posts. The tool also creates personalized cold emails, develops meta tags for various page types, and features a variety of advertising assistance, such as:
- Generates headlines and descriptions for Google Ads
- Develops headlines and primary text for Facebook Ads
- Creates posts and descriptions for Google My Business
- Drafts unique real estate listings
- Builds Tweets and TikTok captions
I couldn’t begin to describe the 50+ features that Jasper offers, but they all work in a similar fashion. Users input some basic information (i.e. about your brand, product, or blog topic) and the AI software will generate the content at the click of a button. You can also request the tool “regenerate” the content if you don’t like it, or give it more specific direction using “commands.”
So, I also put Jasper to the test. And my first impression was great – the tool is easy to use, intuitive, and full of useful templates to try. I found it especially helpful for overcoming writer’s block when I was stuck on a section of an article, and coming up with captivating headlines for my posts. It also was valuable when creating an outline for a blog, with it providing unique angles on a given subject. However, the more I used it, the more I became frustrated with the tool’s output.
Simply put, it was not giving me human-quality content. Jasper often wrote multiple paragraphs of content around the same topic, reinforcing the same exact points in different words, without offering unique value. When I commanded it to find a statistic to incorporate, I found some figures were outdated and I was not given a link to confirm the sources. Occasionally, the tool would go astray and off-topic from the core points of my article, pull in typos, or gather bizarre verbiage from the web.
Because the tool relies on the web to extract and create content, its sources are wide and vast. This is great in that it’s evaluating many different types of content out there; however, it also poses a high risk of compiling misinformation about your topic. The internet is full of misinformation, and when Jasper generates content, it’s hard to know what’s fact and what’s fiction.
With that in mind, I’d recommend using Jasper for:
- Content writing inspiration
- Blog outline development
- Headline ideas
- Short snippets of content, including ad and social post development
But, be wary of longer-form text, statistics, and other information compiled by the tool. Always QA!
3. Frase.io:
Frase is an AI SEO tool that is very similar to Jasper, in that it’s essentially a content writing assistant powered by AI. The system offers a diverse range of SEO and content-focused tools, including (but not limited to):
- An article writer
- Blog title idea generator
- How-to blog post generator
- Blog outline generator
- Meta description developer
- Content re-writer
- Semantic topic research
- Listicle creator, for questions, bullet points, and more
- Product description generator
Frase also offers some additional features for SEO optimization, such as a long-tail keyword research tool, based on SERP analyses, and a Content Analytics feature, based on Google Search Console insights.
As an SEO-focused AI writing assistant, Frase works a little differently than Jasper. Frase actually does some competitive research for you, suggesting and creating content based on the top-ranking search results for your target keyword. Frase also shows you the competitors that are ranking on your topic and enables you to create a content brief or outline inspired by the most successful competitors.
When I put Frase IO to the test, I was impressed with its ease of use, multitude of features, and SEO capabilities. The content it generated for me also read very well and sounded relatively human. However, I still ran into some of the same challenges that I did with Jasper: I questioned whether the content was fully accurate, and more significantly, I was not blown away by the content output.
I ran into very few grammatical issues with Frase, but ultimately found that it contained a lot of “fluff.” Similar to Jasper, there was not a lot of intention and meaning behind the paragraphs. The tool occasionally went astray from what I was hoping to convey in my article. I needed to remove and re-work many of the paragraphs it generated. At the end of the day, I am confident that with a little more time, I could’ve written a much better article from scratch.
With that, I would still recommend using Frase to overcome content hurdles and improve efficiencies when developing an SEO content plan. Specifically, my favorite use cases of Frase were as follows:
- Creating content outlines – Frase not only suggests headlines and subsections for your article, but also bases these suggestions on competitive insights and real-time SERP results. Frase also allows you to pull in statistics, frequently asked questions, semantic keywords, and more into your content briefs – which can be very helpful for freelance writers.
- Overcoming writer’s block – Similar to the other tools mentioned here, Frase IO is great for getting quick blurbs of content created when you feel stuck. This does not only apply to blogs; Frase could also be used to come up with social media post ideas, product descriptions, taglines, YouTube video headlines, and more.
- Developing Featured Snippet blurbs – Frase offers a few different tools that can be useful when going after a Featured Snippet result. It has a tool that generates definitions (enter that all-performing “What is…” pillar page) as well as tools for generating numbered lists, pros and cons, summary bullets, and more. With about 15 percent of all queries showing a Featured Snippet in Google, and with Featured Snippets capturing about 35 percent of total clicks, these Frase features are worth trying out. (Again, with a little QA, of course.)
4. Surfer SEO
Surfer is an automated SEO tool designed to help content creators research, write, and optimize their content for organic search. It is positioned as an “all-in-one” SEO tool that uses artificial intelligence to provide easy-to-understand recommendations for digital marketers. At a glance, however, the tool feels less focused on content generation and more concentrated on the optimization process of web content.
I tried out a few of the key features of Surfer SEO, after taking some time to learn the ropes. Here is a breakdown of the primary tools available in Surfer SEO:
Content Editor
This allows you to optimize your content for SEO purposes. It is not an AI writing tool in its entirety, but rather, an AI-powered editor that is aimed at boosting your search engine rankings. The tool allows you to input your content or article and then scores it on various aspects like word count, headings, number of paragraphs, images, and semantic keyword usage. What I particularly enjoyed was that, on top of the score, it provides you with suggestions for improvement in these areas. It suggests your ideal word count (based on the search results), the types of headings you should be utilizing in your article, and semantic keyword phrases to utilize based on natural language processing.
Surfer’s Content Editor does provide you with unique, snippets of text that you can add to your article, assisting the writing process. For example, for the topic of “AI and SEO,” the tool provided me with suggested content around questions like ‘Will SEO be taken over by AI?’ and ‘How is AI used in SEO?’ In addition, the Content Editor provided competitors that I might reference while writing the article – an important part of any content outline – as well as a review of the content to ensure your article is fully unique (no plagiarism detected!).
Ultimately, I see Surfer’s Content Editor as a wonderful addition to any SEO or content writing toolkit—because it is optimization-focused. It can help you create SEO-focused outlines and refresh old articles that do not meet SEO best practices. However, these features do overlap with previously mentioned tools, like Frase.io, so I would recommend playing with each to decide on your use cases, and which UX you prefer.
Keyword Research
In addition to its robust content editing features, Surfer offers an automated keyword research tool. You type in a focal keyword for your article, and it will generate a range of related topics and topic clusters that you can incorporate into your content. Upon researching “AI and SEO” in this tool, I was given topic clusters relating to AI content generation, machine learning and SEO, how to automate SEO, and more. The tool also allows you to filter by intent and search volume, to help you get the most out of the recommendations. Overall, I found this to be very helpful for another “all-in-one” keyword research tool, but the information provided does overlap with what other SEO tools (like MOZ and SEMRush) provide.
SEO Audit Tool
Surfer’s Audit tool allows you to input any page on the web, as well as focal keywords for that page, and quickly receive recommendations for improved SEO optimization. The Audit tool is AI-driven in that it analyzes data from the top-performing pages in the search results, and provides uniquely tailored SEO recommendations based on those insights. The Audit provides recommendations related to backlink opportunities, internal linking strategy, keyword usage, word count of page, structure of content, load times, and more. This could be a very valuable tool for SEO professionals to find everything all-in-one place. However, the insights might overlap with what you’d find in other solutions, like MOZ, SEMRush, and others.
From my Surfer SEO trial, I found that this could be a great AI-powered SEO tool for existing content optimization, with supplemental features for keyword and competitor research. This tool is definitely geared more towards content creators seeking to better SEO optimize their web pages quickly. However, Surfer is not an entirely “all-in-one” solution. When thinking about all angles of SEO, it falls short of providing in-depth competitor analyses, structured content outlines, internal linking recommendations (and other writing components), coding and schema updates, and more.
5. Grammarly
Grammarly is an AI-powered online writing assistant that has quickly become a part of my trusted content marketing toolkit. Historically, the tool was not an AI content generator but rather a content editor. Grammarly has long-been an excellent tool for reviewing content for spelling, grammar, syntax, clarity, and delivery mistakes. It ensures you are producing high-quality, mistake-free content. And it does this quickly and easily.
All you need to do is paste your content into Grammarly’s online application, and the AI-powered tool gets to work. It underscores any potential grammar, spelling, or punctuation issues, and lets you know when a sentence is not concise. But this is just at the basic level. An upgraded version of Grammarly can provide you with suggestions to enhance the vocabulary and tone used in your article. It can also assess the formality and fluency of the content, re-write unclear sentences for you, and flag any content that is plagiarized. While the free Grammarly plan is limited to very basic and critical content issues, the Premium version offers over 400 types of checks and feedback in real-time.
For the savvy writers looking to create excellent content, Grammarly is a unique and (in my opinion) essential AI content writing editor that will truly hold your work to high quality standards—which, as we’ll get into next, is essential for strong organic rankings.
Recently, Grammarly did launch the beta version of a new tool called GrammarlyGO, which is worth highlighting here. GrammarlyGO integrates into the traditional Grammarly dashboard, whether you have the free or premium version, and provides AI-assisted content ideas when you’re facing writer’s block. You can use it to generate headline and outline ideas for your blog post, or even to craft paragraphs of text. Below are some examples of output I received for this article, from this easy-to-use tool:
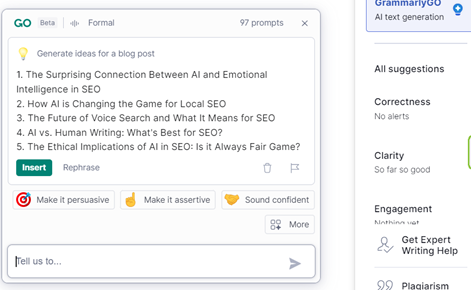
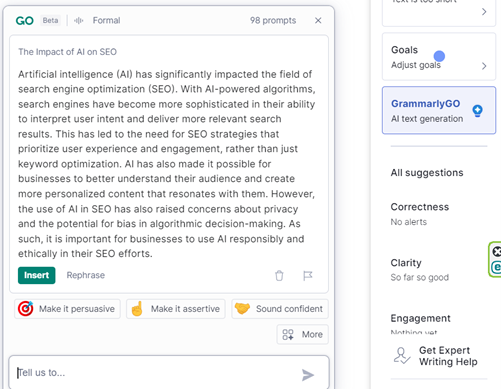
GrammarlyGO’s AI writing assistant can help you to:
- Generate ideas for a blog post
- Write a thank you note
- Craft an engaging email
- Respond to a customer complaint
- Write a marketing proposal
- Draft a sales report
- Announce a new product or service
- Tell a story
And so much more. You can also adjust the tone, level of formality, and goals of the content within this AI tool. However, similar to the other tools listed here, GrammarlyGO does not appear to be founded in SEO best practices. It also does not share its sources of content, which could cause you to question its reliability.
Summary of AI SEO Tools and Use Cases
| Use Case |
ChatGPT |
Jasper AI |
Frase |
Surfer SEO |
Grammarly |
| Keyword Research |
Average |
Not Available |
Great! |
Great! |
Not Available |
| Headline Generation |
Average |
Great! |
Great! |
Good |
Good |
| Content Outlines |
Average |
Great! |
Great! |
Good |
Good |
| Competitive Research |
Suboptimal |
Not Available |
Great! |
Great! |
Not Available |
| Content Writing |
Average |
Good |
Good |
Not Available |
Good |
| Content Editing |
Good |
Good |
Good |
Not Available |
Great! |
| SEO Content Optimization |
Suboptimal |
Great! |
Great! |
Great! |
Not Available |
| Meta Tag Creation |
Good |
Great! |
Great! |
Great! |
Not Available |
| Technical SEO |
Average |
Not Available |
Not Available |
Not Available |
Not Available |
| Social and Email Copy Generation |
Average |
Great! |
Great! |
Not Available |
Not Available |
What Does Google Have to Say About AI and SEO?
Google recently released updated guidance about AI-generated content. In this February 2023 release, they confirmed that automation has long been used to generate useful content, and that there can be value in using AI tools to create helpful, exciting content for your website. However, Google discourages the use of AI tools for creating content for SEO’s sake: “If you see AI as an essential way to help you produce content that is helpful and original, it might be useful to consider. If you see AI as an inexpensive, easy way to game search engine rankings, then no [you should not use AI to generate content].”
Here are some key snippets of Google’s 2023 statement on AI content generation:
“When it comes to automatically generated content, our guidance has been consistent for years. Using automation—including AI—to generate content with the primary purpose of manipulating ranking in search results is a violation of our spam policies…
“This said, it’s important to recognize that not all use of automation, including AI generation, is spam. Automation has long been used to generate helpful content, such as sports scores, weather forecasts, and transcripts. AI has the ability to power new levels of expression and creativity, and to serve as a critical tool to help people create great content for the web…
“Google’s ranking systems aim to reward original, high-quality content that demonstrates qualities of what we call E-E-A-T: expertise, experience, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness… Our focus on the quality of content, rather than how content is produced, is a useful guide that has helped us deliver reliable, high quality results to users for years.”
With this, Google suggests that content creators continue to assess (and prioritize) their work’s quality, authority, and trustworthiness. Quality content is the content that will rank well for SEO, whether it’s generated by a human or by an automated tool. However, when AI-generated content is used to manipulate search engine rankings, that would be against Google’s official Webmaster Guidelines.
Google’s Guidelines for Automatically Generated Content
Google Search Central defines automatically generated content as content that’s been generated programmatically, where it’s intended to manipulate search engine rankings. This might include:
- Text that makes no sense to the reader but which may contain search keywords.
- Text translated by an automated tool without human review or curation before publishing.
- Text generated through automated processes.
- Text generated using automated synonymizing or obfuscation techniques.
- Text generated from scraping Atom/RSS feeds or search results.
- Stitching or combining content from different web pages without adding sufficient value.
If your content falls into any of these categories, Google might flag it as spam. And you might see an effect on your content’s organic visibility (or lack thereof).
Google has a variety of systems, including SpamBrain, that help to detect spam content, however it is produced (by a human or by AI). However, during an Office Hours session in April 2022, John Mueller, Search Advocate at Google, revealed that Google cannot yet tell the difference between AI-generated content and human-written content. If AI-generated content is high-quality and informative (even if it was written for SEO purposes), it can rank very well.
What Google Looks for in Content (No Matter How It’s Produced)
Whether it’s written by AI bots or experienced human writers, Google seeks to rank content that is valuable and informative.
“Focusing on rewarding quality content has been core to Google since we began. It continues today, including through our ranking systems designed to surface reliable information and our helpful content system. The helpful content system was introduced last year to better ensure those searching get content created primarily for people, rather than for search ranking purposes,” writes Google in their 2023 blog post.
Danny Sullivan, a Public Liaison for Search at Google, agreed with this sentiment on Twitter, reminding us: “For anyone who uses *any method* to generate a lot of content primarily for search rankings, our core systems look at many signals to reward content clearly demonstrating E-E-A-T (experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness).”
Google’s Helpful Content Update Aimed at Relegating AI-Written Content
Google has consistently expressed a preference for unique, valuable, and authoritative content. It seeks to rank content that showcases expertise on a given topic and offers a learning experience for its readers. It looks for content that is people-first, designed to educate human readers.
Hence, the release of the “Helpful Content Update,” which was first rolled out in August 2022. The Helpful Content Update is a new, automated, sitewide ranking signal that Google now uses to:
- Demote low-value content that is not particularly helpful to users, and
- Reward websites with high-value, helpful, and people-first content.
The August 2022 roll-out was the first of many Helpful Content Updates. A second was released in December 2022, and Google has stated that more may be on the way: “Over the coming months, we will continue refining how the classifier detects unhelpful content and launch further efforts to better reward people-first content.”
The key word here is “people-first.” Google will devalue websites that have created content primarily for search engines and search traffic, if they are not providing value to real, human readers. The search giant explains: “SEO is a helpful activity when it’s applied to people-first content. However, content created primarily for search engine traffic is strongly correlated with content that searchers find unsatisfying.”
This brings us back to the topic of AI content generation. Why are we using AI? To optimize our content marketing and SEO strategies, right? To churn out more content faster, and meet the growing demands of CMOs to drive organic traffic? At the end of the day, this is the reality. This is how AI is being used. We just have to be careful in how we use it. If AI-generated content isn’t great content—if it’s not helpful, intentional, and unique—it could end up hindering a website’s rankings.
So, how can you assess whether your content is “helpful”? Google suggests asking yourself these questions:
- Is the content primarily to attract people from search engines, rather than made for humans?
- Are you producing lots of content on different topics in hopes that some of it might perform well in search results?
- Are you mainly summarizing what others have to say without adding much value?
- Are you writing about things simply because they seem trending and not because you’d write about them otherwise for your existing audience?
- Does your content leave readers feeling like they need to search again to get better information from other sources?
- Are you writing to a particular word count because you’ve heard or read that Google has a preferred word count?
- Did you decide to enter some niche topic area without any real expertise, but instead mainly because you thought you’d get search traffic?
- Does your content promise to answer a question that actually has no answer?
- Are you using extensive automation to produce content on many topics?
If you answered yes to any of the above, take it as a signal to re-assess your content approach.
Final Recommendations for Using AI in Your SEO Strategy
At the end of the day, it’s safe to say that AI has changed SEO as we know it—and businesses who adopt AI tools to support their marketing strategies are likely to reap the benefits. In the realm of search engine optimization, AI can help to streamline content writing processes and reduce the time it takes to develop SEO-focused topic ideas, article outlines, email outreach, and even coding tasks.
However, after trying out these tools, my stance remains the same. AI-powered content writers and SEO platforms are great assistants. They are helpful support systems. But they are not replacements for humans. AI content writing tools, in particular, are not going to be your token to improved SEO rankings. Google desires content that is written by people, for people—Content that offers unique value, so that readers can walk away feeling their question has been answered. For now, AI is not producing that quality of work. It still needs the human touch.
For the record, I really tried to use AI content writers to compile this article. While I was generally impressed with the ease of use and topic ideas offered by each AI writing assistant, I found the content itself containing a bit too much “fluff.” In other words, the content was not unique. While the AI tools avoided plagiarism, and structured content in a logical way, I was not getting a lot of meaning or purpose behind the paragraphs of text. They felt more like summaries of everything else out there, without driving any single point home. This is, again, because of the way these AI tools work. They compile information from various websites and data sources to create unique content for you. However, AI bots, and specifically AI writing assistants, do not always know how to synthesize that information to develop a coherent story and conclusion.
AI tools also do not (to my knowledge) have a way to ensure accurate information, or ignore bad information—making it difficult for me, the writer, to trust the final output. ChatGPT even admitted this:
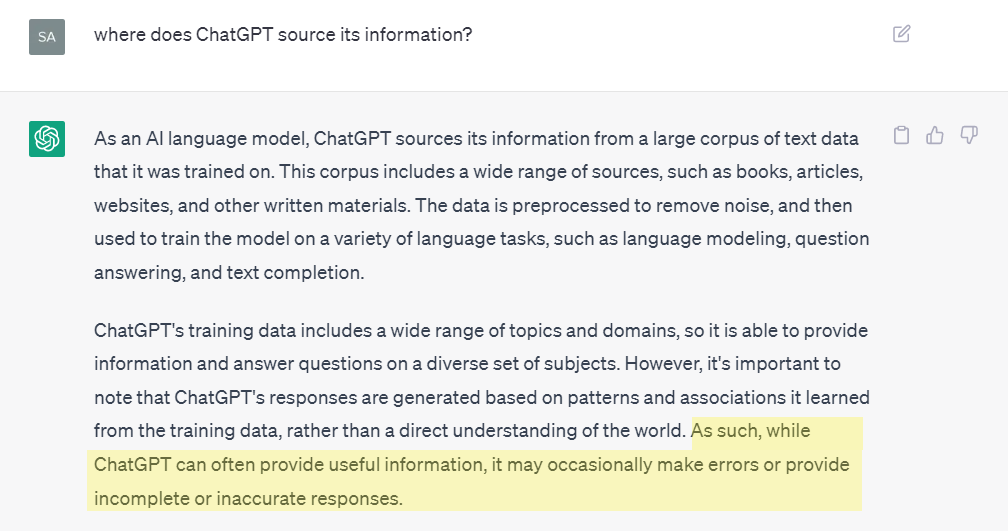
I’ll leave you with this conclusion, an example, written by Jasper AI:
While AI tools can be great writing assistants, they cannot replace human writers. This is especially true when it comes to producing high quality content that meets Google’s standards. Always fact check what AI tools suggest and don’t hesitate to get more professional help if you need it.
Do you want more advice about how to leverage AI or improve your SEO processes? Our team of experts are happy to help you plan your next steps.
If you’re interested in enhancing your SEO strategy, including leveraging AI tools, please contact Synapse by email at sales@synapsesem.com.