The Evolution of Google Ads Match Types

In the realm of online advertising, Google Ads has long been a cornerstone for businesses seeking to connect with their target audience through Pay-Per-Click (PPC) campaigns. Over time, Google has continually refined its advertising platform, including the evolution of match types. While match types initially provided advertisers with greater control and precision, there has been a noticeable shift towards automation, leading to concerns over diminishing advertiser control. In this article, we will explore the journey of Google Ads match types, examine the impact on advertisers, discuss the challenges they face, and review the opportunity this has created for advertisers to grow.
1. Broad, Phrase, and Exact Match
The introduction of broad match marked the beginning of a journey for Google Ads advertisers. Advertisers were excited about the prospect of reaching a wider audience and gaining visibility. However, as broad match keywords cast a wide net, advertisers soon realized that this came at the cost of control and relevance. Ads were displayed for a plethora of unrelated searches, leading to wasted ad spend and diluted campaign performance.
This is where phrase and exact match keywords came in, with the goal of restoring control and precision for advertisers. Phrase match allowed advertisers to target keyword phrases in a specific order by using quotation marks, while exact match ensured ads only appeared for exact keyword matches. Advertisers created many variations of their keywords to ensure they would show up for all relevant searches, including singular and plural variants, as well as common misspellings.
With phrase match and exact match, advertisers could fine-tune their campaigns, reaching a more relevant audience and optimizing their budget for maximum impact. Advertisers gained a sense of control over their PPC campaigns, resulting in improved click-through rates and higher conversion rates.
2. Broad Match Modifiers
Recognizing the need for a middle ground between reach and relevance, Google introduced modified broad match. This match type offered advertisers the ability to include specific keywords within broad match by adding a plus sign (+) before them. While broad match modified expanded reach, it still provided a certain level of control over ad targeting. Advertisers could cast a wider net while maintaining some relevance, striking a delicate balance. However, it was the last significant update that retained a semblance of control before Google’s subsequent emphasis on automation.
3. Close Variants
With the introduction of close variants, Google expanded the boundaries of match types. While this expansion seemed advantageous at first glance, it signified a shift towards automation. Close variants allowed ads to appear for searches that included variations of target keywords, such as misspellings or singular/plural forms. If the keyword the user searched had a similar meaning to the keyword you were bidding on, then your ad would appear. This applied to all three match types, which was significant as that meant exact match keywords were no longer an “exact” match. This decreased advertiser control as searches that may seem like close variants were matching out to keywords that were designed to only match out to an exact variation. This caused a significant increase in the importance of well-managed negative keyword sets.
4. User Intent
With the integration of user intent into the matching process, advertisers now rely on Google’s algorithms to decipher the context and intent behind search queries, matching them to relevant keyword bids. This shift towards automation means that advertisers must trust Google to accurately interpret user intent and deliver their ads to the right audience. While this automated approach brings efficiency and scalability, it also requires advertisers to have faith in Google’s algorithms and data-driven decision-making. Advertisers are encouraged by Google to embrace the role of strategic overseers, focusing on ad copy, targeting strategies, and understanding their audience, while entrusting Google to optimize the matching process based on user intent.
As Google increasingly focuses on automation and machine learning, advertisers have pivoted to taking on a more strategic role in account management. Google’s algorithms take the reins, making decisions on when and where ads appear. This automation brings efficiency and ease of management for advertisers as this allows them to focus on deeper analysis of campaign performance. The evolving landscape of Google Ads match types, coupled with automation, has led to several implications for advertisers:
- Reduced Precision: Advertisers have less control over which specific keywords trigger their ads. As a result, there is a risk of displaying ads to less relevant or unqualified audiences, potentially leading to lower conversion rates.
- Limited Budget Control: With automation playing a more significant role, advertisers may find it challenging to allocate their budget effectively. Automated bidding strategies can quickly deplete budgets without clear visibility into the decision-making process.
- Dependency on Machine Learning: Advertisers must adapt to Google’s increasing reliance on machine learning algorithms. This entails learning to optimize campaigns within the constraints of automated systems, embracing performance insights, and making data-driven adjustments.
- Emphasis on Copy and Strategy: As control over match types diminishes, advertisers need to focus on developing compelling ad copy and refining their targeting strategies to maximize the impact of their campaigns
- Importance of Negative Keywords: With a broader range of search terms being matched out to, effective negative keyword management is critical to success. This ensures that ads are displayed to the most relevant audience, which increases the likelihood of attracting qualified leads and potential customers.
The evolution of Google Ads match types has brought both benefits and challenges for advertisers. While the initial match types provided control and precision, Google’s emphasis on automation and the introduction of close variants have allowed advertisers to save time by not having to build out extremely granular keyword sets that constantly need to be refined. While there is less control by advertisers, there are still ways to ensure they are reaching their target audience through well thought out match type strategies and negative keyword management. Relying on Google to accurately identify user intent has given advertisers more time to focus on strategic initiatives, ad copy development, landing page optimization, and more. Advertisers must adapt to the changing landscape, navigating the complexities of automated systems while finding new ways to optimize their campaigns. Balancing the benefits of automation with the need for customized targeting and precision remains a key challenge in the world of PPC advertising.
Want to learn more about how to navigate the increasingly complex world of PPC advertising? Reach out to the team at sales@synapsesem.com to learn more about our comprehensive services.
Reels. Shorts. TikToks. How The Consumption of Video is Evolving
In today’s digital age, video content has become an integral part of our daily lives. In fact, 93% of social media marketers say video is a vital component of their social media strategy. Video has been a buzzword in marketing for years, and today brands are using it to establish a clear voice and devoted followings on social media. From the rise of YouTube to the emergence of social media platforms like Instagram and TikTok, the way we consume video has undergone a significant transformation. The introduction of short-form videos, such as Reels, Shorts, and TikToks, has revolutionized the way we create, share, and engage with visual content. Keep reading as we explore how the consumption of video is evolving and the impact it has on our online experience.
The Rise of Short-Form Video Content
Short-form videos have gained immense popularity in recent years, capturing the attention of millions worldwide. Platforms like Instagram Reels, YouTube Shorts, and TikTok have allowed users to create and share bite-sized videos that are typically under a minute in length. This format presents an opportunity for content creators to tell engaging stories, share quick tutorials, showcase talent, and entertain their audience in a concise and visually appealing manner. Did you know users will retain 95% of a message watched in a video as opposed to just 10% read in text? This is just one of the reasons that over 54% of marketers argue video is the most valuable content type for achieving social media marketing goals.
Short-Form Video Appeals to Short Attention Spans
One of the driving factors behind the success of short-form videos is the shrinking attention spans of modern audiences. In an era where information is constantly being thrown at us, capturing an audience’s attention quickly is crucial. A recent study from Vidyard found that 58% of viewers will watch the entirety of a business’ video if it’s less than 60 seconds long. Short videos cater to this demand by delivering content that is easily digestible and captivating within seconds. This format encourages creators to be creative and concise, resulting in content that is entertaining and memorable.
Engagement and Interactivity
Another aspect that sets short-form videos apart from other content is the high level of engagement they promote. Social media platforms like TikTok have introduced features such as duets, stitches, and challenges, allowing users to collaborate, remix, and respond to existing content. This interactive nature of short videos fosters a sense of community, encourages user participation, and provides opportunities for creators to collaborate and connect with their audience in unique ways. Viewers feel more connected and invested in the content when they can actively engage with it. In fact, The Sprout Social Index found that 66% of consumers report short-form video to be the most engaging type of social media content in 2022, up from 50% in 2020.
The Democratization of Content Creation
The rise of short-form videos has also democratized content creation. Previously, creating professional-quality videos required expensive equipment, technical skills, and significant resources. However, the accessibility of smartphones with high-quality cameras and user-friendly editing apps has empowered individuals from all walks of life to become content creators. Not to mention the ring light. This new era of content creation has allowed for a diverse range of voices and perspectives to be heard and has opened up new avenues for creativity and self-expression.
How Short-Form Video is Changing the Social Media Landscape
Short-form videos have had a profound impact on the social media landscape. Platforms that were primarily focused on static images and text-based updates are now incorporating video as a central component of their user experience. Instagram introduced Reels as a direct response to the popularity of TikTok. YouTube optimized its platform for shorter videos called “Shorts”. Facebook took a similar approach, introducing their own version of Reels. This shift demonstrates how platforms are adapting to changing user preferences and investing in short-form video content to retain and attract users. Due to higher retention and engagement rates and stronger SEO performance, everyone is vying to be the top platform delivering short-form video content.
The Influence of the Algorithm
Have you ever felt like your social platforms are listening to you? Algorithmic feeds play a crucial role in shaping the consumption of video content. Platforms like TikTok and Instagram use sophisticated algorithms to curate personalized video feeds based on user preferences, behavior, and engagement patterns. By analyzing user interactions, the algorithms present a stream of videos tailored to each individual’s interests, making it easier to discover content that resonates with them. This approach increases the chances of content creators reaching a wider audience, fostering diversity, and exposing users to a variety of video content.
Video Content Monetization Opportunities
The evolution of video consumption has also introduced new avenues for monetization. Short-form videos have provided content creators, or “influencers”, with opportunities to earn income through sponsorships, brand partnerships, and advertising. Influencers and creators with substantial following can generate revenue by promoting products or services within their videos. Additionally, platforms themselves have introduced monetization features, such as YouTube’s Partner Program and TikTok’s Creator Fund, which enable creators to earn money based on views, engagement, and ad placements.
Future Implications for TikToks, Shorts and Reels
As the consumption of video continues to evolve, we can expect further innovations and advancements in the field. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are likely to play a more significant role in the creation and consumption of video content in upcoming years. Live streaming and real-time interactions may become more integrated into short-form videos as well, enabling audiences to engage with creators and influencers in real-time. Furthermore, as technology progresses, we can expect to see improvements in video quality, editing capabilities, and overall user experience. This will likely trigger an even further dependency on short-form video content than we are seeing now. If you want to stand out on social and diversify your social media strategy with video, we recommend being consistent, tracking your performance, and experimenting to see what type of content resonates with your audience.
TikToks. Shorts. Reels. Oh My!
The consumption of video content has evolved significantly in recent years, driven by the popularity of short-form videos, and we can expect to see it continue to dominate. Reels, Shorts, TikToks, and other bite-sized videos have captured our attention, thanks to their succinctness, interactivity, and engagement. These formats cater to the demands of modern audiences, providing easily digestible and captivating content. As platforms adapt to these changes, creators and users alike can look forward to a dynamic and immersive video landscape, where creativity and connection thrive. To ensure you are maximizing the engagement on your videos across platforms, contact us today!
Google Ads Experiments: Key Features & Best Practices
It’s no secret that a/b testing is imperative to a successful paid search program—but what does that mean, and what can it look like? There are several approaches you can take when running tests for your paid search campaigns. Maybe you are testing landing pages, running new ad copy, or trying to determine the best CTA for your target audience. In any case, even the seemingly-smallest Google Ads tests can pay off.
So why exactly should you conduct tests? Below we have outlined some of the benefits of a/b testing for your paid search strategy. We also discuss why running an experiment within Google Ads is a great option, and some of the top considerations when determining the best PPC testing strategy for your organization.
Key Benefits of Google Ads Experiments
-
Continue to Improve Upon Your Paid Search Program:
Not all tests are guaranteed to drive profound and statistically significant results, but the greatest goal and benefit of testing is to identify what works and continue to make it better. Whether your main KPI is impression volume, traffic, conversions, or revenue, running experiments within Google Ads allow you to test things such as ad copy, landing pages, keyword strategy, bidding strategies, extensions, and more. One Synapse client tested a new CTA in their ad copy and landing page messaging and found the new CTA had a 90% higher conversion rate than the original CTA/message.
-
Stay Ahead of Your Competition:
In an ever-changing paid search landscape, your organization must continue to test to get ahead of competition. If you continue doing what you have always done, you will likely start to see declining performance as your competitors are capturing and converting a larger portion of traffic. Use features in Google Ads such as Auction Insights to keep track of how aggressively your competition is bidding on your keyword set and how that aggression changes over time. Other tools such as SEMrush or Google’s new Ads Transparency Center can help you monitor the specific language competitors are using in their ads.
Google Ads Experiment Features:
-
Google’s New “Sync” Feature
In January 2022, Google announced they were reconfiguring the experiment process within Google Ads. With that, they rolled out the “experiment sync” feature, in which, any update made within the control campaign would automatically be made in the test campaign (if opted in). Because it is imperative to keep experiments as even as possible and mitigate extra variables, this feature is great. It keeps your campaigns synced and won’t let a minor adjustment (e.g. a bid optimization) influence the results.
-
Easily Apply Experiment Results in One Click
Along with the experiment updates rolled out in early 2022, Google also made it much easier to adopt testing results with an “apply experiment” button after you have ended your test. To make this decision, Google assists by telling you if you have reached statistical significance, as shown in the image below.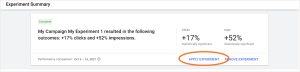
-
Keep Messaging Consistent
If you are testing landing pages with a different call to action or overall theme, it is important that users are exposed to that type of language throughout all steps of their sales journey. This includes Google Ads ad copy, whether it be a responsive search ad or display ad. Ad copy and landing page continuity is critical for user experience and minimizing factors when analyzing your test results.
-
No Reliance on IT or a 3rd Party Platform
One common bottleneck of a/b testing for organizations is the reliance on IT or a 3rd party testing platform to set up a test on the backend. One major benefit of Google Ads Experiments is that you can create experiments within the platform (and your agency partner can completely handle the setup)..
Top Considerations for Google Ads Experiments
Now you’re ready to run with your first Google Ads experiment, but there are still things you have to consider and determine to run your test well. Whether you are just testing the waters with paid search, or looking to level-up your paid search strategy with Experiments, here are a few key considerations to keep top of mind when starting out:
- Have you run any tests before? If so, how did they go?
- What is the main goal of the test?
- What are your competitors doing?
- Do you have enough traffic to generate statistical significance within a reasonable amount of time?
Consider these questions carefully as you determine how to run your next Google Ads experiment. What types of tests have worked well for you in the past? Are there any learnings from prior tests that you can apply to a new test? Think about what you want to accomplish and be sure to prioritize your experiments by estimated impact.
Google Ads Experiments are a great way to conduct a/b tests for your paid search strategy. If you need help setting up your experiment or a consultation on your paid search strategy, please contact us by email at sales@synapsesem.com to talk through your Google Ads testing needs.
How Google’s Infinite Scroll Impacted the SERP for Good
“No one clicks over to Page 2”. We’ve all heard this timeless quip, that no one in their right mind would ever be so bold as to want more than 10 options to find what they’re looking for. Publishers and brands would fight for their page 1 rankings, as this, we were told, was the only way to get in front of organic search audiences.
But things have changed. In December 2022, Google introduced an infinite scroll feature, which automatically loads new results as you approach the end of the page. While this may be a convenient update for users, it’s causing quite a stir among website owners who rely on page 1 click-through rates for traffic. In this article, we’ll delve into the effects of Google’s infinite scroll update and its potential impact on SEO click-through rates and traffic.
What is infinite scroll?
Infinite scroll, or more accurately continuous scroll, is Google’s new SERP functionality that allows searchers to scroll through results past position #10. While not quite infinite – this new functionality requires searchers to click “See More” after the first 60 or so results – this core SERP format update has far-reaching implications for searchers and publishers alike.
This update wasn’t Google’s first foray into the world of stretched SERPs. In October 2021, Google began testing a continuous scroll functionality for mobile devices that would allow cellphone searchers to explore an unending SERP.
How does infinite scroll impact organic CTR?
In the past, Page 1 keyword rankings were the name of the game. The logic went that if it wasn’t on Page 1 of Google, it simply didn’t exist. When applied to large brands and their SEO content, this rightfully concerned anyone aiming to improve their organic search performance. Sure, ranking in position #11 was better than not ranking at all, but data shows that as of November 2022, only 8% of desktop users were clicking on results from Page 2. With the barrier to lower-ranked results now gone, it’s possible your page ranking in position #11 might now generate significantly more traffic.
Whether searchers enjoy Google’s new infinite scroll functionality is still yet to be seen. However, as the curious digital marketers we are, the Synapse team set out to answer a glaring question: how does infinite scroll impact click-through rates by position?
How to Determine Infinite Scroll Click-Through Rates
We devised a plan to answer this question the only way we knew how: by crunching the numbers. (If there’s one thing we love here at Synapse, it’s data-driven insights!). We downloaded two sets of desktop search data from our clients’ Google Search Console profiles: 6 months before the desktop infinite scroll update launched and 6 months after. For each timeframe, we compiled a list of over 80,000 queries, their position, and their CTR. To avoid inflating the data, we filtered out branded queries (including close variants) and any query with fewer than 10 impressions over the 6 month period to avoid any one-search-one-click 100% CTR data points.
We used this data to calculate the average desktop CTR for each position in the SERP. By grouping all non-brand queries ranked in position #3, for example, we could determine the average CTR for this position. A quick pivot table later and we had the average CTR for each rank position charted on a line graph.
The Results
So what did we find? Surprisingly, it doesn’t seem that CTRs for formerly-page 2 positions changed all that much. A quick look at the chart shows that after position #6, the pre- and post-update data look about the same. What did change was CTRs for the top 3 positions. Position #1 seems to have experienced a -33% decrease in its organic click-through rate. Similar trends were seen for most other positions up to #6.
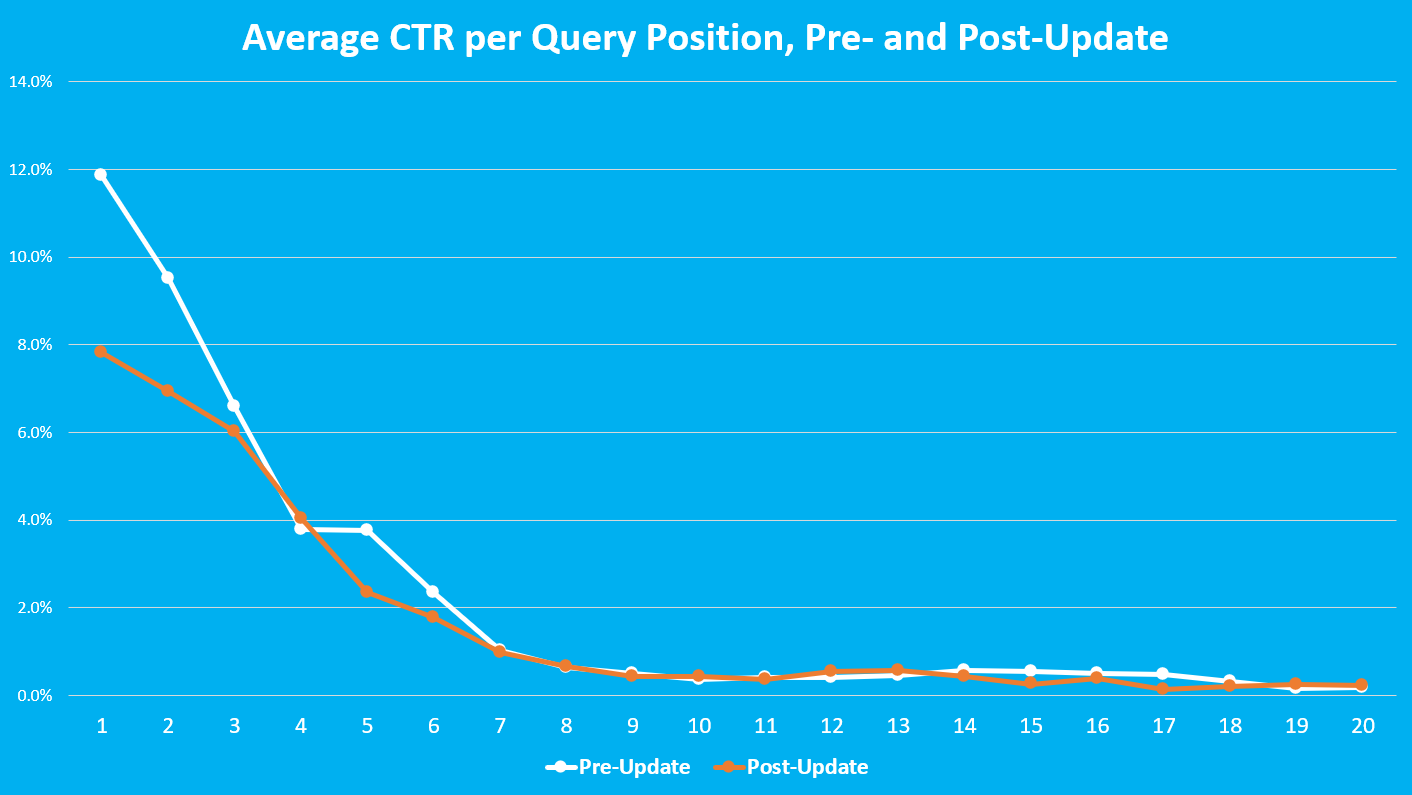
Our analysis suggests that while CTR for positions 1-6 fell on average by 20.8%, the rest of the SERP was mostly unaffected.
Before the update hit desktop browsers, position #1 enjoyed an 11.9% click-through rate, according to our data. In the 6 months that followed, its average CTR fell to 7.8%. Similar narratives played out across the top 6 positions, with each position’s CTR falling, on average, -20.8%.
Conclusion: How Did Desktop Infinite Scroll Impact CTR?
Surprisingly, click-through rates for positions previously located on page 2 seem to have not been affected by the infinite scroll functionality. However, our data suggest that positions #1-#6 now experience decreased click-through rates.
So what happened? While it might be impossible to say for sure, it’s possible that as searchers are faced with more information directly in the SERP – featured snippets and quick answers, but also more titles and meta descriptions – they’re less likely to click on any links at all. The zero-click trend is something search analysts have been discussing for years. This October 2022 analysis from Marcus Tober at SEMrush delves into the growing zero-click search trend in great detail. Our data would support this growing trend, as the total CTR for the top 20 positions decreased from 46.8% to 36.6% after the update.
Regardless, changing click-through rates and increased zero-click searches are trends we’re continuing to monitor at Synapse. In fact, we’re implementing new strategies designed to improve CTRs to help offset any negative impact from zero-click searches. Want to learn more about these strategies and our comprehensive SEO services? Reach out to the team at sales@synapsesem.com.
GA4 POV: Top 3 Benefits and Challenges
Have you recently migrated to GA4 but are still getting up to speed on the actual differences (the good and the bad) between GA4 and Universal Analytics? If so, this blog is for you!
By now we’ve all heard of Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and a majority of us have spent hours and resources migrating to this new and improved platform, but what now? Sometimes change can be difficult and taking the time to learn a new platform when you already have a full plate can be overwhelming. At Synapse, we began migrating our clients to GA4 over a year ago and have taken the time to identify some of the main benefits of this new platform. While we have identified strengths of GA4, those don’t come without challenges which we’re sure you’ll also identify (or already have).
Below we have listed out the top three benefits of GA4 along with the top three challenges we have identified, and what we’re doing to get the most out of the new platform.
Top 3 Benefits of GA4
While many of us are still struggling to learn the ins and outs of this new platform setup, there are some great benefits to GA4 that will up your analytics game:
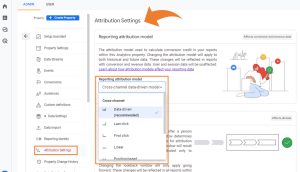
#1. Customizable Reporting Attribution Model Settings
In GA4 you’re able to choose the attribution model that is best for your business from a list of pre-defined options:
- Data-driven (recommended & default)
- Last Click (cross-channel)
- First Click
- Linear
- Position-based
- Time Decay
- Last Click (ads-preferred)
If you remember, the default attribution model of Universal Analytics is/was last non-direct click and only GA360 users had the opportunity to analyze data via other attribution models in all reporting (outside the model comparison tool). This update with GA4 allows users to pick the attribution method that best aligns with their company goals and how any back-end data is being tracked. The attribution model each company picks for their new GA4 property will apply to all of the data within the property (rather than just model comparison). This is significant as users will be able to analyze large amounts of data and various dimensions using their preferred attribution, rather than relying on the limitations of UA’s model comparison tool.
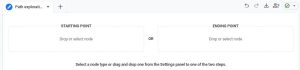
#2. Sophisticated Conversion Path Exploration Reports
Universal Analytics had conversion funnel path exploration reports, but GA4 brings these reports to a new level. While you have access to the “conversion paths” report within the “advertising” section, you can also utilize the Path Exploration template within the explore reports section. This report is extremely helpful and has similar functionality to a normal explore report in that you can add segments, dimensions, and metrics, but there is one feature that takes the cake: reverse path exploration. Within your report, click “start over” in the upper righthand corner. This brings you to a blank screen in which you can “start” the report by identifying your ending point first and follow the conversion path backwards, a long-awaited Google Analytics capability. For example, you can now view who filled out a free trial form on your site and exactly which actions they took and pages they visited leading up to this conversion. These findings can aid in marketing decisions, site testing, and much more.
#3. Highly Customizable Interface
While UA’s “Custom Reports” have been replaced with “Explore” reports (more on this later), you can also customize the entire left-hand rail of the Reports section. Are there certain views you constantly look up and you need the ability to drill down? You can go to the “library” and create your own reports under the Lifestyle section, User section, or a net new section (called a Collection). In addition to adding new reports, you can update what is brought into the default reports or even delete reports altogether. For some of our clients, we have hidden the revenue/e-commerce reports as they don’t apply to their business. These reports will be visible to everyone with access to the property so customizations should be fully thought out.
Honorable Mentions:
- You can track your website and app (if applicable) in the same property (previously a combination of UA and Firebase).
- Access and own your raw data via a free BigQuery export. Standard properties can export 1 million events into BigQuery without incurring costs, after which the user owns that data and is able to manage, manipulate, and use it after the data retention period set within GA4 has passed.
- GA4 is set up with better and more intelligent user privacy capabilities. Some features GA4 rolled out to protect user privacy are IP anonymization and the ability to opt in/out of several data collecting mechanisms like ads personalization.
Top 3 Challenges of GA4 (and what to do about them)
We’ve gone over some of the main benefits of GA4 but in full transparency there still are some challenges with the platform. Before we get too set on these challenges, though, know that GA4 is still new and Google has consistently been rolling out updates and improved functionality, so they may not be challenges forever! Let’s get into it:
#1. Explore Reports Can’t Drill Down
If you’re like me, I used to use Custom Reports in UA for almost everything to assure I was only looking at what I wanted and could drill down to very specific data points. This isn’t as easy with explore reports as drill-down functionality doesn’t yet exist, meaning each of your dimensions must be visible at the same time. Because of this, we recommend being very strategic with filters applied to your explore report to negate the data you don’t care about. If the analysis is something you are likely to use often, we also recommend updating the available reports via the library, as discussed previously.
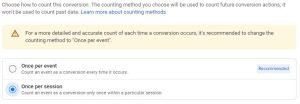
#2: Conversions Are Counted Differently
If you’re comparing conversions between GA4 vs. GA3, you may notice that GA4 is reporting a higher number. This is partially because all conversions within GA4 are events and are defaulted to count “every” event versus each unique event. Recently Google rolled out the option to change the counting method to “once per session” for events marked as conversions which we recommend switching to for most sites. If you do not switch to this counting method, we recommend you analyze conversion volume by analyzing sessions where a conversion event occurred (filtering for event name), rather than relying on the “conversion” metric, to assure you are analyzing unique conversions.
#3: No Google-Supported Way of Preserving Your UA Data
Google has announced that non-360 Universal Analytics accounts will stop collecting new data in July 2023 and that they will delete the Universal Analytics data in July 2024. Users have been forced to migrate to GA on their own and figure out what to do about losing their data. Luckily there is something you can do about this to assure your data is not lost! At Synapse we have developed ADE, Analytics Data Extractor. With this system, we can extract five years (or more) of your Universal Analytics data, house it within BigQuery and populate Looker Studio reports to assure you have access to your historical data. Accessing this data is important for several reasons, the biggest being context into past performance and anomalies to explain and guide future marketing decisions.
Google Analytics 4 is here to stay and while it may be a learning curve there are a lot of great benefits from the platform! If you or your organization need help with your GA4 migration, please reach out to us through the contact form on our website! Further, if you are interested in saving your Universal Analytics data, schedule a demo with our team to learn more about our process and schedule your extraction date!