The 5 Best Google Ads Scripts in 2025

Google Ads scripts offer advertisers a powerful way to automate workflows, optimize campaigns, and uncover hidden performance insights. With programmatic access to your account’s data and settings, these scripts help streamline repetitive tasks, enable data-driven decision-making, and improve efficiency.
With so many options available, here are our five must-have scripts that can take your Google Ads reporting and optimization to the next level:
1. Customize budgets by day of week
Google Ads automatically adjusts your monthly budget to maximize clicks and conversions, but sometimes, you need more control. If your account follows predictable weekly patterns—like lower weekend conversions—you might prefer to set exact daily budgets.
That’s where Ambrie’s Budgets by Day of the Week script comes in. It lets you customize the exact amount you want to spend, by campaign, for each day of the week. While you could achieve similar results with Google Ads rules, the script’s Google Sheet interface makes it easier to adjust daily allocations on-the-fly without dealing with the complexity of the rules platform.
At Synapse, we’ve enhanced this capability by integrating the script with our new suite of reporting tools. By using monthly pacing data to pinpoint where we get the most efficient conversions by day and campaign, we’ve fully automated the budget optimization process, saving time and improving accuracy.
2. Analyze RSA copy performance
Analyzing Responsive Search Ads (RSAs) can be challenging without the right tools. Google Ads only allows performance exports for individual ad units, meaning advertisers managing granular ad group structures might face hundreds of manual exports to get a complete picture of headline and description performance.
Digital Oasis’s RSA Performance script eliminates that bottleneck. By adding this script to your Google Ads account, advertisers can bulk export performance data for every headline and description across all enabled ad units, ad groups, and campaigns in just minutes, saving time and helping uncover valuable performance trends at scale.
Not only can this script reveal which headlines and descriptions drive the best results, but it also shows which types of copy resonate most across different keyword themes and campaigns. With these insights, you can refine your messaging, double down on high-performing assets, and improve the effectiveness of your RSAs without the manual workload.
3. Control close variant query matches
Google’s keyword match types have evolved, with new “close variants” expanding exact and phrase match keywords to include plurals, misspellings, synonyms, and related terms. Although these close variant queries can be helpful in capturing additional reach, they can sometimes cause irrelevant search term traffic to match out to your ads, wasting ad spend on low-converting terms.
While you can control close variants with regular search query monitoring and negation, the Exclude Close Variants script can put that process on auto drive. The script monitors and automatically negates close variants to ensure that you’re only showing on the very specific queries that are built into your keyword set.
4. Monitor search query trends
Query monitoring is an essential part of any Google Ads manager’s job. In addition to identifying irrelevant queries to negate, regular monitoring can uncover trending search terms that highlight new opportunities for growth. However, with so many queries coming through every day, combing through the data can be a difficult task.
Nils Rooijmans’s Trending Search Term script simplifies this process by tracking weekly, monthly, and yearly shifts in query traffic automatically . This allows you to quickly spot trends, helping you target high-potential keywords and eliminate irrelevant ones.
5. Improve PMax data transparency
Since Performance Max (PMax) campaigns were introduced, advertisers have benefited from their fully automated, goal-based bidding capabilities. However, one significant disadvantage of the campaign type is the limited in-platform visibility into performance by placements, queries, and channels. This lack of transparency has made it difficult for advertisers to determine where their dollars are the most efficient in generating conversions, in turn limiting their ability to optimize campaigns effectively.
Mike Rhode’s PMax script tackles this issue by accessing hidden data from the Google Ads API to uncover granular performance insights. The script has several useful features, including channel cost and conversion breakdowns, search query analysis, and detailed asset performance reporting. By installing this script, advertisers can take advantage of the machine-learning benefits of PMax while gaining the data and control needed for advanced reporting and campaign optimization.
Google Ads scripts can transform how you manage and optimize campaigns, automating tedious tasks and uncovering valuable insights. But implementing and managing them effectively takes time and expertise.
Need help setting up or customizing scripts to fit your specific needs? Reach out to us at sales@synapsesem.com to learn more about our comprehensive services.
Guide to the GA4 BigQuery Export
 The switch from Universal Analytics to Google Analytics 4 (GA4) has come with both benefits and challenges for marketers. One of the most exciting benefits on the data analysis and warehousing front is the free (no 360 required!) BigQuery link.
The switch from Universal Analytics to Google Analytics 4 (GA4) has come with both benefits and challenges for marketers. One of the most exciting benefits on the data analysis and warehousing front is the free (no 360 required!) BigQuery link.
This link allows you to seamlessly export your GA4 data into Google BigQuery—a powerful, fully managed, and serverless data warehouse in the Google Cloud Platform. By combining the capabilities of GA4 with the analytical prowess of BigQuery, you can unlock a wealth of possibilities for extracting valuable information from your data.
In this guide, we’ll explain how to leverage the BigQuery GA4 Export to its fullest potential. You’ll explore its advantages and discover how to set up the export, understand its data schema, and harness the power of BigQuery SQL queries to derive meaningful insights from your GA4 data.
Why Should I Export GA4 Data to BigQuery?
In the world of digital analytics, collecting data is just the first step in the journey toward meaningful insights. The true power lies in your ability to extract valuable information, identify trends, and make informed decisions. GA4 is a powerful tool in its own right, but to supercharge your data analysis, you should consider exporting your GA4 data to Google BigQuery for the following reasons:
- Integrate GA4 data with other sources: To gain a comprehensive view of your business performance, it’s best to combine your GA4 data with other sources. BigQuery offers seamless integration with various data connectors, making it possible to merge your GA4 data with advertising data from Google Ads, your CRM, or even external datasets. With all your data integrated, you can build customized audience segments, explore traffic attribution, and build simple machine learning models.
- Accelerated Data Visualization: For those dealing with sluggish GA4 data load times in BI and data visualization tools like Google Data Studio, Google BigQuery is a game-changer. The BigQuery BI Engine smartly caches frequently used data, drastically speeding up SQL queries and boosting the efficiency of data visualization and Business Intelligence tools. This translates to faster insights, smoother interactions, and an overall more responsive experience.
- Automate repetitive tasks: One of the biggest efficiency-boosters of using BigQuery is the ability to automate repetitive analyses and data pulls. By setting up automated queries and reports, you can eliminate the need for manual data extraction and analysis, saving valuable time and resources.
- Advanced analysis: BigQuery is a powerful tool that supports advanced analytics and machine learning applications, enabling you to delve deeper into your data. You can perform complex analyses, conduct predictive modeling, and identify trends that might have remained hidden.
- Avoid sampling and thresholding: The BigQuery export contains raw data from GA4. This allows you to bypass data limitations you may see in the GA4 platform, such as sampling, cardinality, and thresholding.
To fully reap the benefits of the GA4 BigQuery export, it’s essential to set up the link as soon as possible. The export isn’t retroactive, meaning the sooner you create your link, the sooner you start accumulating valuable historical data.
How to Link GA4 and BigQuery
The first step to exporting your GA4 data to BigQuery is setting up a Google Cloud account. Google Cloud offers a free tier that includes 10 GB of data storage and up to 1 TB of querying each month. For most small to medium-sized businesses, this free tier provides more than enough resources to get started with a GA4 export to BigQuery.
Once you have your Google Cloud account set up, make sure that your Google account has “Owner” permissions in Google Cloud and at least “Editor” permissions in GA4. After you complete these initial steps, you can move forward with enabling the BigQuery link from the Google Analytics admin tab:
- Navigate to BigQuery Links under the Product Links menu in your property settings.
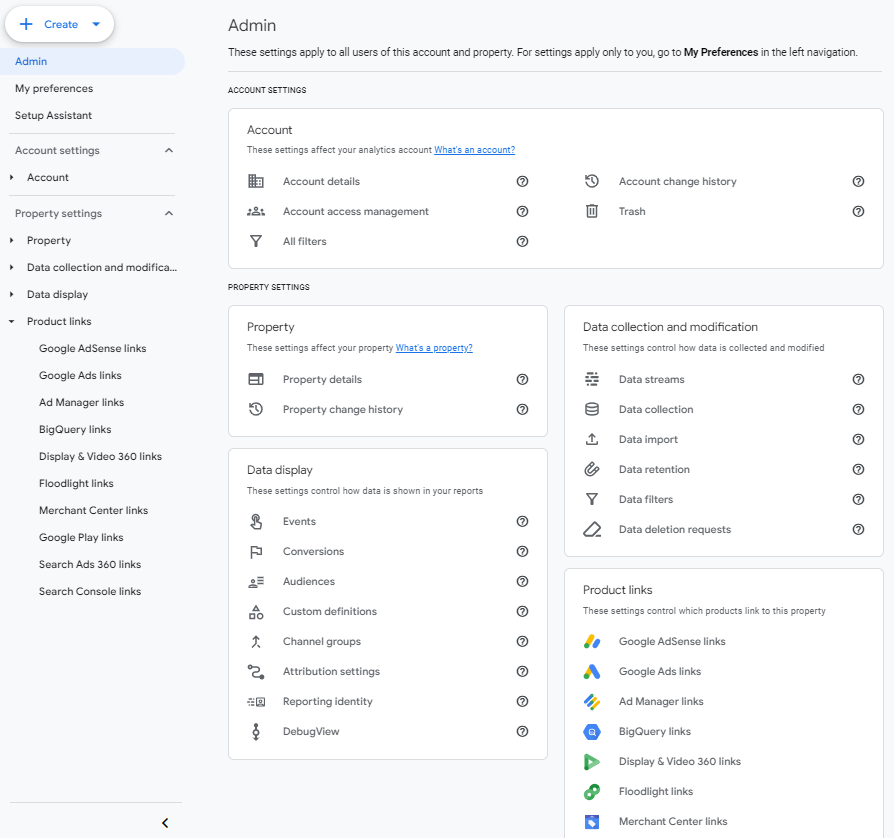
- Click Link to create a new connection.
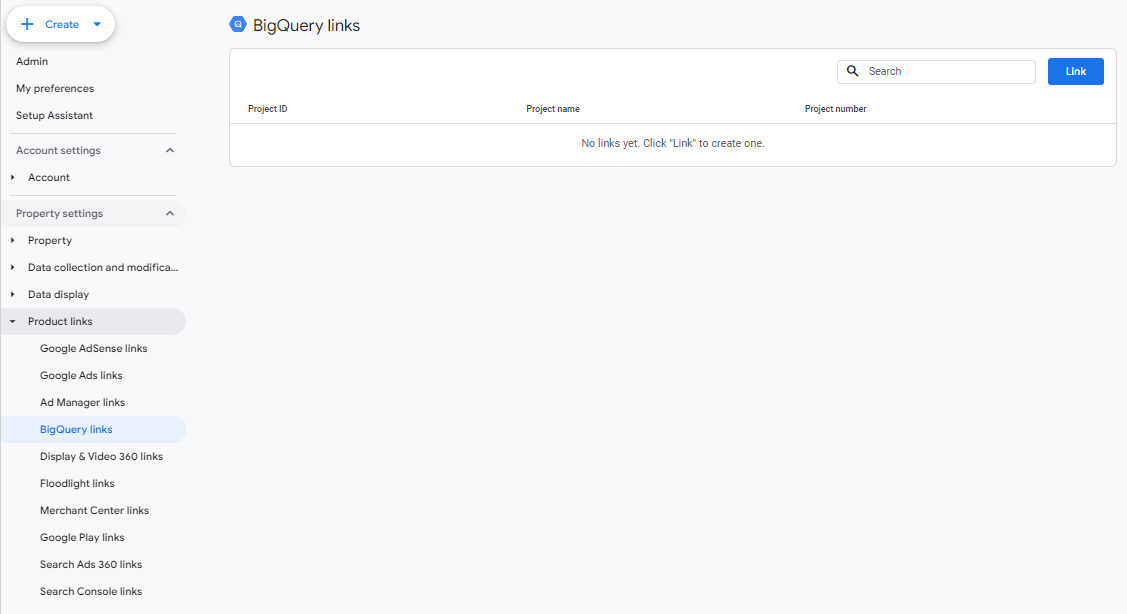
- Click Choose a BigQuery project to see the list of projects you have access to. Select the project you want the export to be housed in and click Confirm.
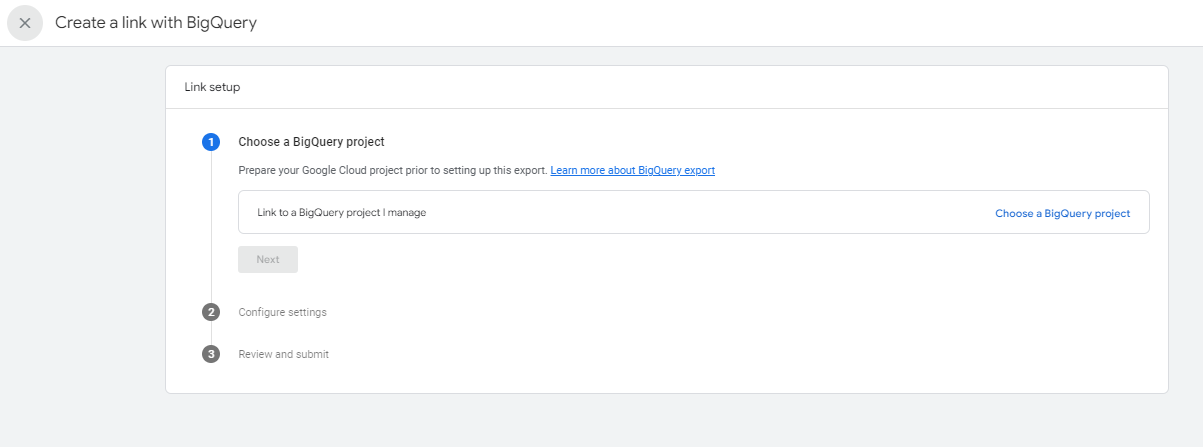
- Select a location for the data and click Next.
- Configure your settings. You can choose which data streams to include with the export and specific events to exclude from the export under Configure data streams and events.
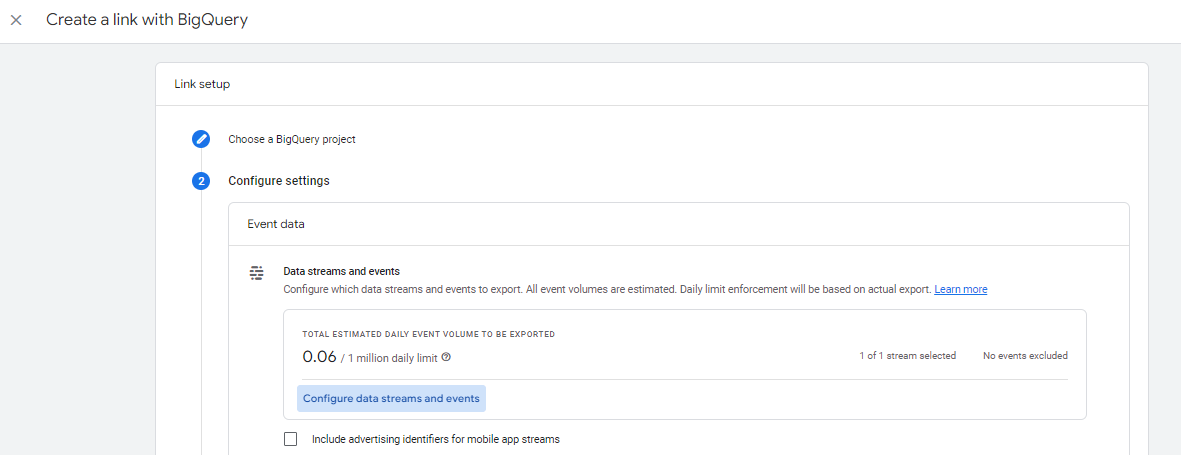
- Choose the types of tables you want to export. The Event data export is event-scoped, whereas in the User data export, each row represents a unique user. You can also choose the frequency of your Event data export: “Daily” for once a day and optional “Streaming” where the current day’s data will be stored and can be accessed immediately.
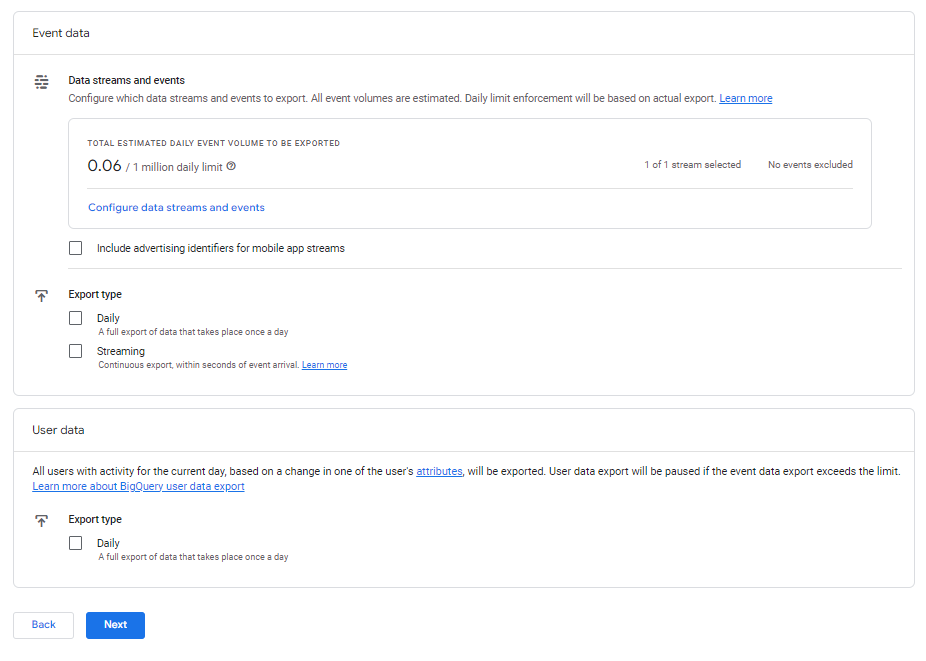
- Review your settings, then click Submit to finish setting up your link.
Once the link is created, it can take up to 24 hours for your data to appear in BigQuery. For daily exports, a new table will be exported each day that contains the previous day’s data.
Understanding the Data Schema
Now that you’ve set up your link, the next step to unlocking the benefits of the GA4 BigQuery export is understanding the structure of the data.
Tables
For Event data exports, a table named events_YYYYMMDD is created each day if you have enabled the Daily export option. If you’ve also chosen to export streaming data, you’ll see another table named events_intraday_YYYYMMDD, which is continuously populated as events are recorded throughout the day.
The User data export will create up to two new tables. The table named pseudonymous_users_YYYYMMDD contains rows for every pseudo user ID, excluding users who have not consented to cookies. If you’ve set up user ID collection for your website and are sending that data to GA4, you will also see users_YYYYMMDD tables, which include data for unconsented users. For both User data table types, rows are updated when there is a change to one of the fields.
Data Schema
The columns in each table type represent the parameters that are available for querying. Google has provided detailed explanations of each parameter for both the event data export and the user data export in their documentation.
How to Query and Analyze Your BigQuery GA4 Data
Now that you’ve set up your link and gained an understanding of data schema, it’s time to put your data to work. SQL is the language used to interact with the tables in your BigQuery dataset, and it offers a standardized way to communicate with your data. Here’s how to access the built-in query editor in BigQuery:
- Login to Google Cloud Console: Go to the Google Cloud Console and sign in with your Google account.
- Access BigQuery: In the Cloud Console, click on the navigation menu (☰) in the top-left corner and select “BigQuery.”
- Select Your Project: Ensure you have the correct Google Cloud project selected in the project dropdown at the top of the BigQuery Console.
- Write SQL Queries:
- Click on your dataset on the left-hand panel, where you have your GA4 data stored. Select the table you want to query.
- Click the “Query” button. This opens a pane where you can write and execute SQL queries.
If you’re just getting started with SQL, there are many free resources online to help you learn the language, such as Codeacademy and Datacamp. A great resource for generating GA4 BigQuery queries specifically, without writing any SQL of your own, is GA4 SQL. This tool allows you to select the metrics, dimensions, and filters you want to apply to the raw data export and paste them as-is into the query editor. Google has also provided some basic and advanced queries in their Query Cookbook for Google Analytics to help you get started analyzing your data.
As you become more comfortable with SQL, you can modify and create custom queries tailored to your specific business needs. SQL is a versatile tool that empowers you to interact with your data and uncover valuable information, whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user.
If you’re eager to harness the benefits of exporting your GA4 data to BigQuery, you can also reach out to Synapse SEM for help. Our team of experts can handle everything, from setting up the export to creating comprehensive reports and analyses that provide actionable insights. Contact us by email at sales@synapsesem.com or by phone at 781-591-0752 to get started.
What is the Google Product Reviews System, and What Does it Mean for Your Digital Marketing Strategy?
Reviews are incredibly impactful – and essential – for business marketing and profitability. According to a recent study, over 99% of online shoppers refer to reviews when making purchase decisions, making them the top factor impacting consumer choices. (Source: Power Reviews)
However, reviews don’t just influence buying behavior – they can also boost your business’ online visibility. Reviews have become a significant component of both paid and organic search marketing strategies, with Google rolling out a series of updates that reward review content in search results.
If you want to stay ahead of the competition, it’s time to start prioritizing reviews in your marketing strategy. In this guide, we review Google’s product reviews system, its impact on digital marketing, and how you can make the most of this algorithm update.
What is the Product Reviews System?
The Google product reviews system is designed to reward review content that is most helpful and useful to searchers. Periodically, Google releases an update to the system, called a product reviews update. The latest February 2023 product review update is the sixth in a series of releases that date back to April 2021.
According to Google’s documentation, the product reviews system is aimed at providing searchers with reviews that include “in-depth research, rather than thin content that simply summarizes a bunch of products.” Rankings may improve after a product reviews update if Google deems the product review as having “content that provides insightful analysis and original research” written by “experts or enthusiasts who know the topic well.”
Any site that publishes review content may be impacted, including:
- Merchant sites with shopper guides
- Independent blogs
- News or other publishing sites
Currently, the product reviews system affects searches in the following languages globally: English, Spanish, German, French, Italian, Vietnamese, Indonesian, Russian, Dutch, Portuguese, and Polish. These updates do not consider user-generated content, like reviews on a product page.
How Does the Product Reviews System Work?
The product reviews system is based on Google’s machine learning algorithm, which uses hundreds of signals to identify “helpful” reviews. Many of these signals are focused on the quality of the review content. According to a blog post from Google software engineer Perry Liu, the system is designed to reward content that:
- Includes helpful in-depth details, like the benefits or drawbacks of a certain item, specifics on how a product performs, or how the product differs from previous versions.
- Comes from people who have actually used the products, and show what the product is like physically or how it’s used.
- Includes unique information beyond what the manufacturer provides — like visuals, audio, or links to other content detailing the reviewer’s experience.
- Covers comparable products, or explains what sets a product apart from its competitors.
The product reviews system machine learning algorithm may use structured data to understand if a site includes review content. However, structured data is optional and not the only indicator used to identify reviews online.
Content is evaluated by search engine crawlers primarily on a page-level basis. However, site-wide assessments may be made on domains that contain a high percentage of product review content. In other words, if your website does not have many reviews, you’ll only see pages that contain this type of content rewarded by these updates.
The product reviews system requires a periodic refresh from Google. In the past, updates have been anywhere from two to eight months apart. This means you might not see immediate improvements after improving or creating new content. Rather, sites need to make changes and wait for the next update to see rankings improve. Google’s John Muller also explained that the product reviews algorithm might be incorporated into the overall web search rankings at some point. In this case, we should expect to see quality reviews be rewarded on a more consistent basis.
How Can you Benefit from the Most Recent Product Reviews Update?
The most recent February 2023 update to product reviews system has shown a preference for review content across many high-volume, product-focused queries. Since its release, we’ve seen robust review content monopolizing the first-page search results. For one B2B software client, 70% of the SERP on their top sales-driving keyword is review content. This has created a higher level of competition on the SERP.
Even if your website does not focus on review content, you may still be able to take advantage of the next product review update to gain visibility on key terms for your business. There are two ways to benefit from review content as a business selling a product:
- Have your products featured on existing 3rd party review websites, such as Capterra or Software Advice
- Create your own review content to rank on Google organically
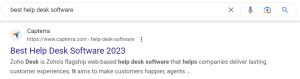
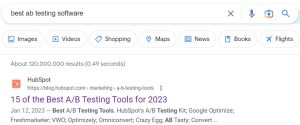
1. Using Capterra to Benefit from the Product Reviews Updates
Capterra is a comprehensive database and search engine that customers can use to browse software options and read user reviews. As one of the largest and most trusted websites dedicated to software reviews, it’s no surprise that Capterra has been affected by product reviews updates. You’ll find Capterra, or other Gartner websites like Software Advice or GetApp, ranking on page one of Google for pretty much any “best” software query.
The chart below shows an increase in estimated traffic to the Capterra website right after the release of the September 2022 product reviews update.
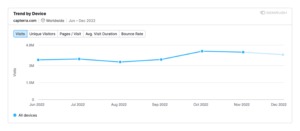 Source: Semrush
Source: Semrush
Software companies can take advantage of Capterra’s rankings by running paid ads on their review pages. The Capterra Ads program allows you to bid on the top positions for their software category pages.
 Source: Capterra
Source: Capterra
Advertisers set their bid to receive clicks to their website, with the highest bidders shown in the highest positions on Capterra’s page. Organic listings for products within the category are still present, but they appear further down on the category page. Capterra’s highly specific categories and large user base make it an excellent option for lead generation, especially as the product reviews system continues to reward their website with top rankings on Google.
2. Creating Review Content on Your Own Product
If you want to grow organic traffic to your website, and stay afloat in the current search landscape, you may consider producing your own review content to rank on Google. With the most recent product reviews updates, we’ve seen companies rank with their own high-quality review content that features their products.
For example, A/B testing software provider HubSpot has been able to rank in the #1 position for the following query as of March 2023.
In the ranking article, HubSpot recommends their tool at the top of the list of products, with reasons why a potential customer should choose their product over others. The article then mentions their competitors in a ranked list, with the benefits and drawbacks of each software.
Of course, there are risks to mentioning competitors’ products in an article like this. Just remember that, when creating your own content, you get to control the narrative.
For Google to recognize your content as high-quality and valuable to customers, you must thoroughly discuss each option with in-depth research. This means that you must examine each competitor’s benefits, and not just the drawbacks, which may give customers reasons to choose the competitor’s product over your own.
On the other hand, creating high-quality review content may bring increased visibility to your website with the next product reviews updates release. You can also control messaging on your product and your competitors, directly speaking to why a customer might choose your product over others.
If you choose to create your own product review content, we recommend that you:
- Follow Google’s best practices for high-quality review content (more on this below).
- Be thoughtful about which competitors you choose. Since Google recommends you include in-depth research for each option, consider choosing indirect competitors you would not mind discussing in detail. These competitors may fit only partially into your product’s category, have a product that does not include all the features your product does, or do not target your business’s key audiences.
- Review other listings in the SERP to identify key sections to include and new areas to focus on (that others aren’t doing already).
- Include informational sections (such as a “What is…” intro or an FAQ section) to establish your expertise and include additional content for SEO purposes.
- Target a word count of at least 1,000 to 2,000 words.
Best Practices for Creating Product Review Content
When creating product review content to rank on Google, it’s important to ensure that it contains in-depth, helpful research. Low-quality content that simply summarizes the information you can find on the manufacturer’s website will not be rewarded by a product reviews updates. Google has provided the following list of guidelines for writing product reviews:
 Source: Google
Source: Google
To make adhering to these best practices easy, we recommend following this structure:
- Establish your expertise: Discuss the general features of the product category and identify the key features that users should be looking for.
- Recommend your product as the best option: Include supporting evidence and showcase the things that make your product stand out from the crowd.
- Rank your competitors: Briefly mention the pros and elaborate on why their cons make their product subpar or consider using indirect competitors to avoid mentioning competition directly.
- Recommend your product again: Discuss again why your product is the best overall, as evidenced from your ranking list. Use additional credibility boosters, such as customer quotes. Include links for users to convert.
If you have any questions about the product reviews system, or if you’d like assistance creating review content or managing a Capterra campaign, you can also contact Synapse SEM. Contact us by email at sales@synapsesem.com or by phone at 781-591-0752.